This disease is poorly studied, although several thousand observations with diagnosis and subsequent treatment have been described.
A lot of diversity and non-specificity of the clinical image of varicose veins of the basin lead to raw errors of the diagnosis, which affects the consequences in the future.
Characterization of varicose veins of a small pool
The veins in the basin are several times longer than the arteries, which determines their great capacity.This is due to the phylogenesis of the vascular system of the pelvic region.The basin veins have high adaptation capacities and are potentially predisposed to restructuring, which contributes to the formation of a densely intertwined network.
The speed and direction of the blood flow are regulated by valves, which are controlled by complex humor mechanisms.The valves balance the pressure in different parts of the venous network.
When the valves stop performing their functions, the stagnation of blood develops, this leads to the pathology of blood vessels and the formation of varicose veins.The unique character of the small basin veins lies in the fact that the large ligaments of the uterus, which support the light of the broad ship, can also reduce it, causing a pathology.
Causes
The pathological dilation of the basin veins can be due to the following reasons:
- Violation of blood exit paths;
- Venous cannon prison;
- Compression of collateral trunks by the modified position of the uterus, for example, in retroflexia;
- Ovary insufficiency of the valve (congenital or acquired);
- Post-stematic obstructive syndrome;
- Pathology of connective tissue;
- Arteriovenous angiiodisplasia;
- Sitting prolonged, hard physical work;
- Varicose veins of the lower limbs;
- Pregnancy (3 or more) and childbirth (2 or more);
- Diseases in the female genital zone (chronic salpingoboophoritis, ovarian tumors, uterine fibroids and genital endometriosis);
- The adhesive process of pelvic organs;
- Obesity.
Degree classification of the disease
In terms of extended vein, the following degrees are distinguished:
- Up to 0.5 cm, a "corkscrew" vascular stroke;
- 0.6-1 cm;
- Over 1 cm.
Options for the course of the disease
- Varices of the perineum and the vestibule of the vagina;
- Complete venous syndrome of the basin basin;
Symptoms
- The most common pain - frequent at the bottom of the abdomen, the perineum after long static and dynamic surfaces.Pain intensifies in the second phase of the cycle, after hypothermia, fatigue, stress, exacerbations of various diseases.
- The feeling is "not comfortable", pain with sex and after.
- Dysmenorrhea - menstrual disorders, including pain syndrome.
- Secretation, more than normal, galls of genital tracks.
- The stagnation of blood leads to infertility, inability, to the interruption of pregnancy.
- Violations of urination following the expansion of the veins of the bladder.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the disease only by complaints only succeeds in 10% of cases.
The palpation of the internal walls of the basin makes it possible to feel seals and oblong nodes of veins.When examined in the mirrors, the cyanosis of the vagina mucosa is visible.
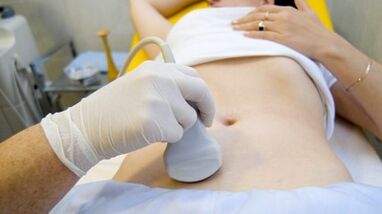
The procedure of choice is an ultrasonic study with color doppler map, which allows you to identify not only extensions of varicose veins of ovarian veins, but also venous thrombosis, post-trombophlebitic occlusion.With ultrasound, it is visible, "towards", the structure without reflection of the signal, located on the lateral surface of the uterus.
The effect of the Doppler study is based on the "dye" of the blue and red color, the venous and arterial blood, corresponding.
The ultrasonic examination apparatus using a special program recognizes the movement of the sensor blood and in the other direction, calculates the speed of the blood flow and the type of vessel.
But the exact definition of the vein is where the artery remains behind the doctor.The Doppler method works in almost all cases, our body dictates exceptions to rules, because the blood flowing from the heart is not always arterial and vice versa.
Thus, an ultrasonic diagnostic doctor sees a arterial or venous vessel, his size, his blood flow and many indicators that an ordinary person does not need, but plays an important role in the possibility of diagnosing.To do this, use transabdominal and transvaginal sensors.
In 5.7% of cases, the disease is recognized by accident during screening.Normally, the diameter of the ovaric vein is 0.4 cm.
CT and MRI have great precision.By using these methods, you can find accumulations of varicose veins in the ligaments of the uterus, ovaries and around these organs.It is possible to determine concomitant pathology.
A very reliable method is a phlebographic study.
The contrast is carried out at the height of the Valsalva sample, against the blood flow.This allows you to see a failure of the valve.
Retronenoscopy on the left, renal phlebography, super sequene phlebarioscopy and phlebariography on both sides are also used.These methods allow you to determine the hemodnam and anatomical changes in the renal veins and the places of falling into the gonad veins.
Super phlébarioscopy is made by catheterization of the gonad veins through a counter-attotal femur or a subclavian vein, with the subsequent introduction of contrast.
Most of the blood of the Plexus Varique without Cornet is thrown through the ovarian vein.But under hypertension conditions, it occurs in uterine veins not horny in the inner iliac vein.The plexus of the veins, through which the exit can occur, includes the sacred and the plexus of the bladder.
In the phlebo -icigography left left, 3 steps of venous stagnation are distinguished in the gap plexus of the left ovary:
- There is no outing of the plexus of the left ovary where it is carried out along an additional short path.
- There is an additional long path.
- Two additional output paths or an additional and auxiliary are visible.
At 2 and 3 steps, varicose veins of the right ovary cluster plexus form.
Laparoscopy is used for differential diagnosis.The pathologically convoluted veins are in the ovary, towards the round and wide ligaments.They look like large cyanotic conglomerates with a slim and tense wall.
The complexity of the diagnosis lies in the fact that the disease is often hidden behind the signs of the inflammatory process, is distinguished by clinical manifestations, masked under endometriosis, prolapse of internal organs, postoperative neuropathies and many extragenital diseases.
Treatment
The main objective of treatment is to eliminate reflux in the veins.In the early stages of the disease, conservative treatment is used.In the late stages of the disease, the treatment of choice is surgery.
Preservative
It consists in normalizing the tone of the veins, improving hemodynamics and trophic processes.
Symptomatic treatment to eliminate individual symptoms.Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory for pain, with bleeding - hemostatic therapy.
The main drugs in conservative treatment are vintage drugs and antiplatelets.
Phèbotonic - Improve the tone of the vascular wall and improve blood flow.With this disease, it is best to consult a gynecologist on certain drugs.
An important method is physiotherapy exercises.
Surgical treatment
- Variques of Renaissance.
- Gonado-Cavalry Shunting.
- Sclerosis for laparoscopy.
- Occurrence of ovarian veins using radiographic methods -ndovascular.
Folk remedies
Since most of the occurrence of the disease is the weakness of the valve device, all the folk remedies that are used for the expansion of the varicose veins of the lower limbs are also used for this pathology.
The most commonly used: ordinary hazel, hops, nettles, chestnut on horseback, dandelion root, tea mushroom, willow, oak, hook of Saint-Jean, series, flower pollen and many other plants.
Effective is: Treatment with oak baths, chestnut, willow, chamomile, pharmacy, drying herbs, must of Saint-Jean.
Prevention
- The first thing to do if there are complaints, predictors or diseases listed above - contact a gynecologist.
- It is necessary to normalize the work regime and to rest, try not to stay in a vertical position for a long period of physical tension.
- Perform exercises for prevention "pedal", "standing pile", "foot foot"
- Adhered to food: eat foods with a high content of vitamins E, R, C, try to eat only white meat, less fat, replace it with fruits, vegetables, cereals.
- Drink a sufficient amount of liquid, but no less than 1.5 liters per day.
- Get rid of excess weight, bad habits.
- Consult the attending physician to wear compression linen, this will improve the flow of the blood of the lower limbs, so there will be less stagnation in the basin.
- Avoid baths, saunas, hammams, hot baths.
In order not to get sick with such difficult disease, it is necessary to follow the preventive recommendations listed above.Treat your health as the most precious of life.
At the slightest suspicious symptom that you cannot get rid of for several days, you should consult a doctor.He must provide you with highly qualified help and save you from suffering.